Pain and Physical Therapy
Physical Therapy is considered one of the best ways to treat multiple types of pain because it focuses so much on treating the root cause and not just the symptoms. Combining hands-on treatments like orthopedic manual therapy with proven pain management techniques like dry needling while progressing through therapeutic exercises brings patients better long-term relief.
The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) describes pain as “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage.” When we are presented with something that causes pain, if capable, we rapidly or reflexively pull out. The tactile sensation of pain is called nociception.
Pain is an awkward inclination that lets you know something might be wrong. It may be consistent, pounding, wounding, throbbing, squeezing, or depicted in many other ways. Now and again, it’s simply an annoyance, like a migraine. At different times it tends to be debilitating
According to John Hopkins, medical pain can bring about other physical symptoms, like nausea, dizziness, weakness, or drowsiness. It can generate emotional consequences like anger, depression, mood swings, or irritability. In certain cases, pain could completely change your way of life and affect your job, relationships and independence.
There are two categories to classifying pain
- Acute Pain
- Chronic Pain
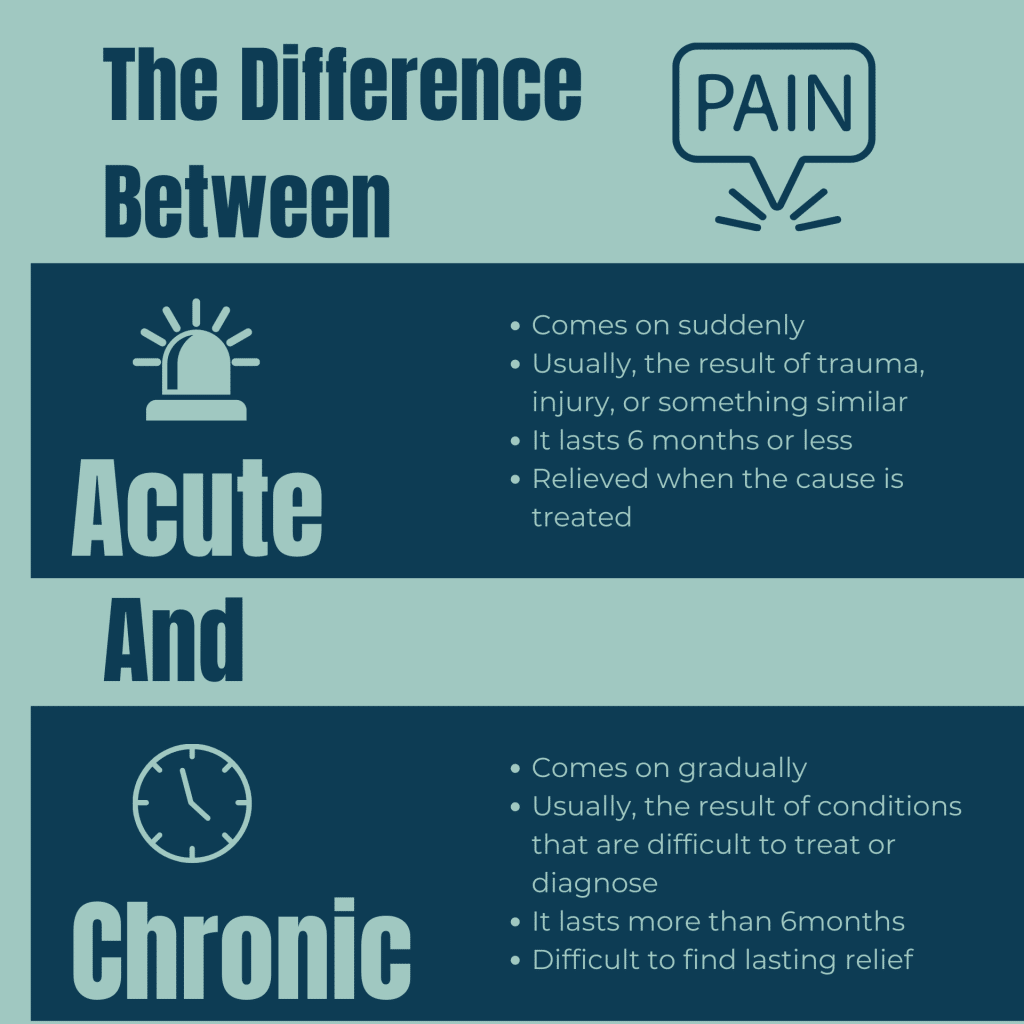
Acute Pain
It usually happens rapidly and disappears. Acute pain generally comes on abruptly and is brought about by something explicit. It is sharp in quality. For the most part, intense agony doesn’t endure longer than a half year. It disappears when there could be, at this point, not a basic reason for the aggravation. Acute pain ordinarily begins unexpectedly after a physical injury, a cut, wound, or muscle injury. Acute pain can likewise be brought about by fever, inflammation, and menstrual cramps. Acute pain is regularly treated by educating the patient, medication, exercise-based recuperation/physical therapy, chiropractic massage, or dynamic development programs.
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is continuous and, as a rule, endures longer than a half year. This pain can continue even after the injury or disease that caused it has recuperated or disappeared. Certain individuals experience chronic pain in any event when there is no previous injury or issues. According to Cleveland Clinic, Chronic pain is linked to conditions that include:
- Headache
- Arthritis
- Cancer
- Back pain
Chronic pain is normal; it influences 1 of every 5 grown-ups and is the number one cause of disability globally. Chronic Pain is a quiet pestilence that diminishes personal satisfaction, adversely impacts connections and occupations, and causes depression. (Sessle, 2012).
Types of Back Pain
According to the Health Policy institute, back issues are patients’ most regular complaints to their primary care physicians. Almost 65 million Americans report a new episode of back pain. Approximately 16 million grown-ups – 8% of all grown-ups – experience industrious or constant back pain, which has restricted them from carrying out certain activities in their everyday life. Back pain is the 6th most exorbitant condition in the United States.
There are three types of back pain; Axial Pain, Referred Pain, and Radicular Pain.
Axial Pain:
Also known as mechanical pain. Axial pain is usually restricted to one specific spot or region in the lower back area. Axial pain is patients’ most common type of lower back pain.

Referred pain
This is a type of pain that is not restricted to one specific region it tends to move around, and the intensity of the pain often varies. Referred pain is the type of pain that a patient faces in one part of the body which is influenced by an injury or discomfort in another part of the body.
Radicular Pain
According to spine health, radicular pain can be described as electric shock-like or burning; radicular pain follows the way of the spinal nerve as it leaves the spinal canal. This sort of aggravation is brought about by pressure as well as irritation to a spinal nerve root. In the lower back (lumbar spine), radicular pain might go into the leg. Different expressions for radicular pain are sciatica or radiculopathy (when joined by shortcoming or potentially deadness). It very well may be brought about by conditions, for example, a herniated plate, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis.
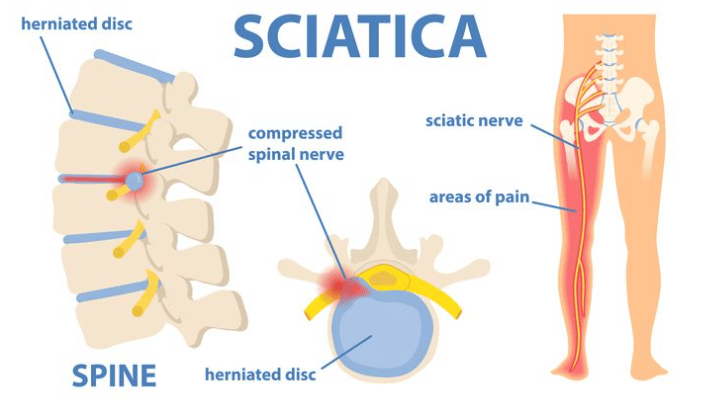
Click here to read more about Sciatica
Types of Neck Pain
Neck pain is torment in or around the spine underneath your head, known as the cervical spine. Neck pain is a typical side effect of previous injuries. According to the Cleveland Clinic, Neck pain is extremely normal. It happens in around one out of three individuals no less than one time each year. It is more normal in ladies than in men, and the possibility of developing neck pain increases with age.
According to UpToDate Patient education: Neck pain (Beyond the Basics), The most common causes of neck pain are Cervical strain, Cervical spondylosis, Cervical discogenic pain, Cervical facet syndrome,
Cervical Strain
A cervical strain is one of the most common issues that is being faced today. This usually occurs the neck muscles suffer an unusual injury. Cervical strains are usually caused due to sports-related injuries with heavy impact and physical/mental stress in everyday life, including poor nutrition and poor posture. Cervical strains last up to 4-6 weeks; neck muscles’ most common cervical strain symptoms are stiffness and tightness.
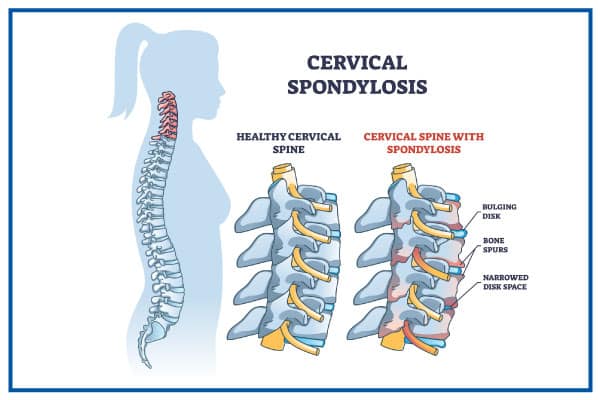
Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical Spondylosis is a condition brought about by unusual cervical spine tears (degenerative changes). The most common symptoms of cervical spondylosis are neck pain, headaches, numbness, and little to no neck mobility.
Cervical Discogenic Pain
This type of neck pain might be the most widely recognized reason for neck pain. It is brought about by degenerative changes in the structure of at least one of the discs in the middle of the cervical vertebrae. The most common symptoms are pain in the neck while turning or shifting your head.
Cervical Facet Syndrome
The facet joints are situated on the sides of the vertebrae, and arthritis in this space can cause pain in the center or side of the neck; certain individuals additionally notice pain in the shoulders, around the shoulder blades, at the foundation of the head, into the ear and jaw, or in one arm. A typical reason for cervical facet syndrome incorporates a task requiring an individual to expand the neck repeatedly in their daily life.
Diagnose and Treating Your Pain
There are endless possibilities to modify a physical therapy treatment program in order to relieve your specific back or neck pain. At Balanced Physical Therapy, our Doctors are licensed and certified to diagnose the exact cause of your pain symptoms. We take a unique 1-on-1 approach to each treatment session to ensure that all our patients receive our undivided attention and are properly progressing throughout all phases of the rehabilitation. Visit our contact page to schedule an evaluation or to find out more about our doctors, treatments, and network of insurances.