Joint Pain & PT
Joint pain can be a debilitating condition that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. It can make moving, walking, or even carrying out simple tasks difficult. In this blog, we will explore some common causes of joint pain, the role of physical therapy in treating joint pain, and some of the most effective joint pain relief strategies.
Causes of Joint Pain
There are many possible causes of joint pain. Some of the most common causes include arthritis, injury, overuse, and infection. Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation in the joints. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Joint Pain From Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the joints over time. It is more common in older adults and can affect any joint in the body.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The condition is characterized by the gradual breakdown of joint cartilage, which can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. The physiology behind osteoarthritis and joint pain is complex and involves several factors.
The joint comprises several components, including bones, cartilage, synovial fluid, ligaments, and tendons. The articular cartilage, the smooth, shiny surface covering the bones’ ends, helps reduce friction and absorb shock during movement.
In osteoarthritis, the articular cartilage begins to break down, which can cause the bone to rub against the bone. This can lead to the formation of bone spurs, which can further exacerbate joint pain and inflammation.
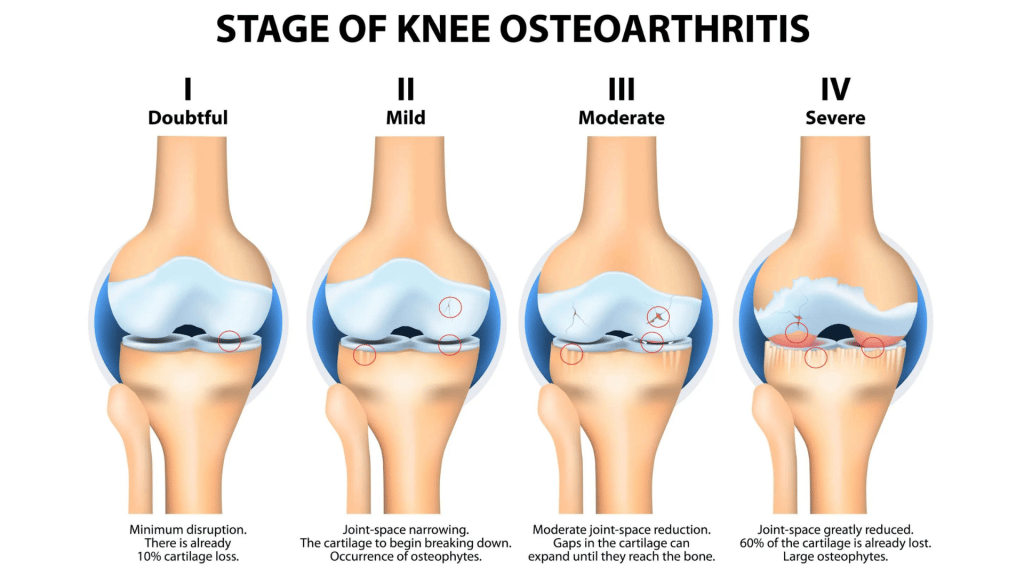
Several different factors can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis and joint pain. Some of the most common factors include the following:
- Aging: As we age, the cartilage in our joints may begin to break down, which can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Genetics: Some people may be more susceptible to developing osteoarthritis due to genetic factors.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can put extra stress on the joints, which can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Injuries: Joint injuries, such as a torn ligament or a broken bone, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Repetitive stress: Repetitive stress on a joint, such as overuse or engaging in certain sports or activities, can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
In addition to these factors, several physiological processes can contribute to developing osteoarthritis and joint pain. These include:
- Inflammation: Inflammation plays a key role in the development of osteoarthritis. When the articular cartilage begins to break down, the body’s immune system may respond by releasing inflammatory chemicals, which can cause pain and swelling in the affected joint.
- Mechanical stress: Mechanical stress on the joint can also contribute to the development of osteoarthritis. When the joint is subjected to repetitive stress, the cells within the articular cartilage may become damaged, leading to cartilage breakdown and osteoarthritis.
- Altered biomechanics: Altered biomechanics, such as abnormal joint alignment or muscle imbalances, can also contribute to the development of osteoarthritis. These factors can put extra stress on the joint, which can accelerate the breakdown of the articular cartilage.
Joint Pain From Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the joints and causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. It can affect people of any age and often affects the small joints in the hands and feet.
In RA, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, which is the tissue that lines the joints. This attack leads to inflammation and thickening of the synovium, causing it to produce more synovial fluid than normal. As a result, the joint swells and becomes stiff, leading to joint pain and reduced mobility.

In addition to inflammation, RA can also cause damage to the cartilage, bones, and other tissues within the joint. This damage occurs due to persistent inflammation, which can wear away at the cartilage and erode the bones.
Injury is another common cause of joint pain. This can include acute injuries, such as sprains or fractures, and chronic injuries, such as repetitive strain injuries. Overuse can also cause joint pain, especially in people who engage in repetitive activities or sports.
Physical Therapy for Joint Pain
Physical therapy can be a highly effective way to manage joint pain. Physical therapists are trained to evaluate and treat musculoskeletal conditions, including joint pain. They can work with patients to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes exercises and other interventions to help reduce pain and improve function.
Physical therapy can be very helpful for patients with joint pain, as it can address the underlying causes of the pain and help improve joint mobility and function. Some ways physical therapy can help patients with joint pain include:
- Pain management: Physical therapists can use various techniques such as heat/cold therapy, manual therapy, and electrical stimulation to reduce pain and inflammation in the affected joint.
- Strengthening exercises: Physical therapists can prescribe specific exercises to help strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joint. Stronger muscles can help support the joint and reduce stress, which can help reduce pain.
- Range of motion exercises: Joint pain can sometimes cause stiffness, making it difficult to move the joint. Physical therapists can help patients improve their range of motion with exercises designed to increase flexibility and decrease stiffness.
- Education: Physical therapists can educate patients on reducing stress on the affected joint in their daily activities. For example, they can teach patients proper body mechanics, posture, lifting, bending, and carrying techniques.
- Assistive devices: Physical therapists can recommend using assistive devices such as braces, splints, or crutches to help support the affected joint and reduce pain.
Overall, physical therapy can be a very effective treatment option for patients with joint pain. By addressing the underlying causes of the pain and improving joint function, patients can often experience significant pain relief and improved quality of life.
Joint Pain Relief Strategies
Many other strategies can also be used to help relieve joint pain. Some of the most effective strategies include:
- Exercise: As mentioned earlier, exercise can be an effective way to manage joint pain. Working with a physical therapist or primary healthcare provider is important to develop an exercise program that is appropriate for your specific condition and needs.
- Weight management: Being overweight can put extra stress on the joints, which can lead to pain and inflammation. Losing weight can help to reduce this stress and improve joint function.
- Heat and ice: Applying heat or ice to the affected joint can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Heat can help to increase blood flow to the joint, while ice can help to reduce swelling.
- Massage: Massage can help to reduce muscle tension and improve circulation, which can help to reduce pain and inflammation in the affected joint.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can effectively manage mild to moderate joint pain. Prescription medications, such as corticosteroids or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), may be needed for more severe cases.


